Cctv Power Supply,Linear Actuator Accessories,Handset Supply,Power Supply ZHEJIANG XINYI INTELLIGENT DRIVING TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.xinyiactuators.com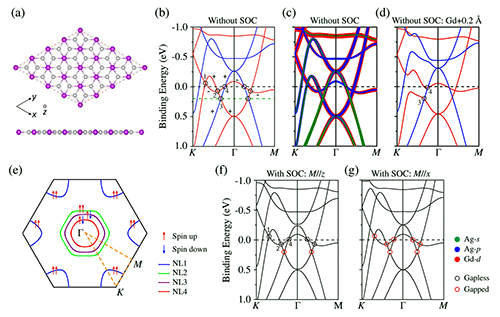
Physics, etc. found in a single layer of ferromagnetic material
[ Instrument Network Instrument Development ] In the past ten years, the topological theory of energy belts has developed rapidly. At present, a variety of topological band structures have been discovered, such as the Dirac cone, the Weyl cone, and the Dirac/Weyl nodal line. Such topological band structures can bring strange physical phenomena, such as chiral anomalies and large magnetoresistance. However, in addition to graphene, which has long been proven to possess a two-dimensional Dirac cone, such peculiar topological band structures are very rare in two-dimensional materials. We know that two-dimensional materials have great application value in nano-microelectronic devices, so it is of great practical significance to realize topological band structure in two-dimensional materials. Feng Baojie, researcher of the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences/Beijing National Research Center for Condensed Matter Physics, researchers Chen Yu and Wu Kehui have long been engaged in the growth and physical property of two-dimensional materials. In recent years, they have made a series of progress in experimental exploration of two-dimensional topological materials. For example, they found a two-dimensional Dirac cone similar to graphene in silene and borene, and then they first discovered a two-dimensional Dirac line in a single layer of Cu2Si.
However, several of the two-dimensional topological materials mentioned above are non-magnetic and are difficult to apply directly to spintronic devices. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the topological band structure in magnetic materials. In 2017, for the first time, two-dimensional ferromagnetic materials (CrI3, Cr2Ge2Te6) were obtained experimentally, which triggered a research boom in this field. However, it is still difficult to achieve topological two-dimensional ferromagnetic materials.
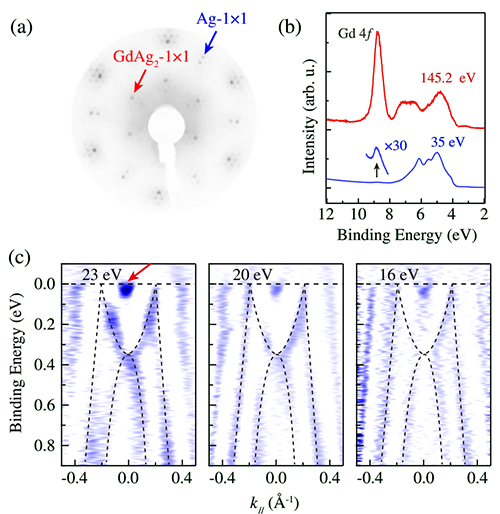
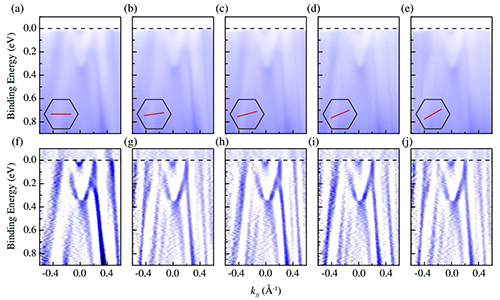
Recently, Feng Baojie, Chen Yu and Wu Kehui collaborated with Professor Yao Yugui of Beijing Institute of Technology and Professor Hiroshima of Hiroshima University in Japan to synthesize ferromagnetic materials in a single atomic layer using simultaneous radiation angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES) combined with theoretical calculations. In GdAg2 (Tc≈85 K), a spin-polarized pilex is found. Through in-depth analysis, they found that these extrapolation lines are protected by crystal symmetry and therefore have good stability. In addition, some of the outer nodes in the single layer of GdAg2 selectively open the energy gap depending on the direction of magnetization.
This work was recently published in the Physical Review Letter (Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 116401 (2019)). The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology, and the B-class pilot program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.